Import Data
Use the File menu to open a data file. See the file formats page for supported formats. Example data files can be loaded by selecting File>Open Example Data.Annotate Rows/Columns
Annotate columns or rows based on entries provided in a tab delimited text file or an Excel .xls or .xlsx file. A colored bar visually identifies members of the same category. Annotatotions are primarily used for visualization. In analyses such as marker selection, column annotations can also be used to identify phenotypes. To annotate columns/rows:- Create a tab delimited text file or an Excel .xls or .xlsx file.
- Select File>Annotate Columns or File>Annotate Rows and open the file created previously.
New Heat Map
To open a new heat map on a subset of your data:- Select the desired columns and rows.
- Select Tools>New Heat Map.
Preferences
Select GENE-E>Preferences (Mac) or View>Options (other platforms) to modify the title, look and feel of the current visualization tool. GENE-E displays a window which provides options specific to the current visualization tool. Most options are self explanatory. The color tab controls the colors used in the heat map:- Relative: GENE-E converts values to heat map colors using the mean and maximum values for each row or the standard deviations from the row mean for each row (as determined by the settings on this tab).
- Global. GENE-E converts values to heat map colors using the minimum and maximum values in the entire data set (as determined by the settings on this tab).
Sorting
You can sort columns by column name, category, or annotation. You can sort rows by row name, category, annotation, or the values in a particular column. To sort columns:Select Tools>Sort Columns.
Select the field(s) to sort by. Each drop-down list includes column (for column name) and all categories and annotations that you have loaded (in this example, the Phenotype category).
To sort rows:
Select Tools>Sort Rows or click on a row header (shift-click to add a secondary sort).
Select the field(s) to sort by. Each drop-down list includes row (for row name), each column name, and all categories and annotations that you have loaded.
Mask Data
Masking rows or columns temporarily hides them from many GENE-E operations. For example, masked rows and columns can be omitted from new heat maps (Tools>New Heat Map). Highlight one or more rows or columns. Select Tools>Mask Rows or Tools>Mask Columns. Alternatively, right-click and select Mask Rows or Mask Columns from the context menu. You can clear masked columns/rows by highlighting one or more columns/rows and selecting Tools>Unmask Columns or Tools>Unmask Rows or to clear all masked columns/rows select Tools>Clear Column Mask or Tools>Clear Row Mask.Marker selection
Marker selection identifies objects that are differentially expressed between two classes. For each object, the analysis uses a test statistic to calculate the difference in expression between the classes and then estimates the significance (p-value) of the test score. It then corrects for multiple hypotheses testing (MHT) by computing both the false discovery rate (FDR) and the family-wise error rate (FWER). The output of marker selection consists of:- Score: The calculated value of the test statistic.
- p-value: The estimated significance of the test statistic for this row (not yet corrected for MHT).
- p-value low: The estimated lower bound for the p-value.
- p-value high: The estimated upper bound for the p-value.
- FDR(BH): The expected proportion of non-marker genes (false positives) within the set of genes declared to be differentially expressed. It is estimated using the Benjamini and Hochberg procedure. (Benjamini, Y. and Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological). 57(1): p. 289-300.1. 1995.)
- FWER: The probability of having any false positives.
Hierarchical Clustering
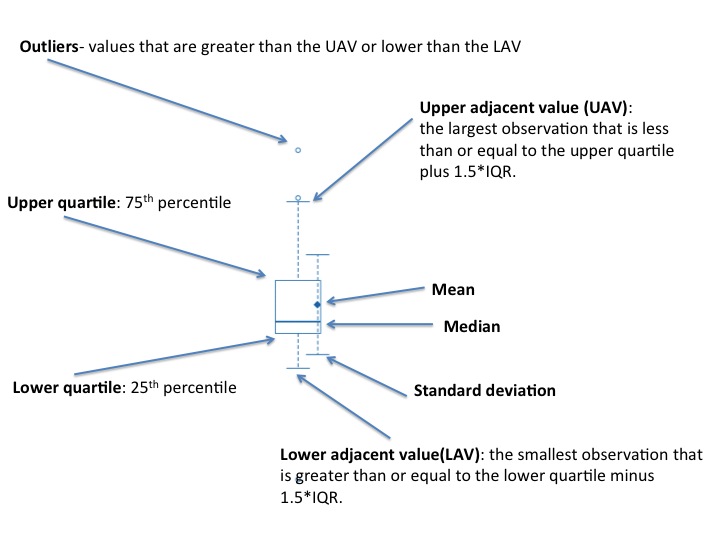
Hierarchical clustering recursively merges objects based on their pair-wise distance. Objects closest together are merged first, objects furthest apart are merged last. The result is a tree structure, referred to as a dendogram, where the leaf nodes represent the original items and internal (higher) nodes represent the merges that occurred.Boxplot