Difference between revisions of "Data formats"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<p><span style="">For sample files, see [http://wwwdev.broad.mit.edu/gsea/resources/datasets_index.html http://wwwdev.broad.mit.edu/gsea/resources/datasets_index.html] or, from within GSEA, select </span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">Help>Show GSEA Home Folder</span></code> and go to the </span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">examples</span></code> subfolder.</span></p> | <p><span style="">For sample files, see [http://wwwdev.broad.mit.edu/gsea/resources/datasets_index.html http://wwwdev.broad.mit.edu/gsea/resources/datasets_index.html] or, from within GSEA, select </span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">Help>Show GSEA Home Folder</span></code> and go to the </span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">examples</span></code> subfolder.</span></p> | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Expression data formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Expression data formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | ||
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#GCT_File_Format </span><span style="">GCT: Gene Cluster Text file format (*.gct)]]</span><span style=""></span><span style=""></span></p> |
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#RES_File_Format </span><span style="">RES: ExpRESsion (with P and A calls) file format (*.res)]]</span><span style=""></span><span style=""> </span></p> |
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#PCL_File_Format </span><span style="">PCL: Stanford cDNA file format (*.pcl)]]</span><a href="#_PCL_File_Format"><span style=""></span></a><span style=""> </span></p> |
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style="">Note</strong>: The GCT & RES expression formats supported by GSEA are identical to those supported by GenePattern.</span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style="">Note</strong>: The GCT & RES expression formats supported by GSEA are identical to those supported by GenePattern.</span></p> | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Phenotype data formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Phenotype data formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | ||
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#</span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">CLS_File_Format:_Categorical</span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";"> </span><span style="">CLS: Categorical (e.g tumor vs normal) class file format (*.cls)]]</span><span style=""></span><span style=""> </span></p> |
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#</span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">CLS_File_Format:_Continuous</span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";"> </span><span style=""></span><span style="">CLS: Continuous (e.g time-series or gene profile) file format (*.cls)]]</span><a href="#_CLS_File_Format:_Continuous"><span style=""></span></a><span style=""> </span></p> |
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Gene set database formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Gene set database formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | ||
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#GMX_File_Format </span><span style="">GMX: Gene MatriX file format (*.gmx)]]</span><span style=""></span><span style=""></span></p> |
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#GMT_File_Format </span><span style=""></span><span style="">GMT: Gene Matrix Transposed file format (*.gmt)]]</span><span style=""></span><span style=""></span></p> |
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#GRP_File_Format </span><span style=""></span><span style="">GRP: Gene set file format (*.grp)]]</span><span style=""></span><span style=""></span></p> |
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#MDB_File_Format </span><span style=""></span><span style="">MDB: Molecular signature database file format (*.mdb)]]</span><a href="#_MDB_File_Format"><span style=""></span></a><span style=""></span></p> |
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style="">Note</strong>: Typically, you use the GMX or GMT formats to define gene sets.</span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style="">Note</strong>: Typically, you use the GMX or GMT formats to define gene sets.</span></p> | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Microarray annotation formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Microarray annotation formats<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | ||
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#CHIP_File_Format </span><span style="">CHIP: Chip file format (*.chip)]]</span><span style=""></span><span style=""> </span></p> |
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#CSV_File_Format_.28for_Chip_Files.29 </span><span style="">CSV: Comma Separated Version (*.csv)]]</span><a href="#_CSV_File_Format_(for Chip Files)"><span style=""></span></a><span style=""></span></p> |
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Ranked gene lists<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong style=""><span style="font-size: 14pt;">Ranked gene lists<o:p></o:p></span></strong></span></p> | ||
| − | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""></span>< | + | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="font-size: 12pt; font-family: "Times New Roman";">[[Data_formats#RNK_File_Format </span><span style=""></span><span style="">RNK: Ranked list file format (*.rnk)]]</span><a href="#_RNK_File_Format"><span style=""></span></a><span style=""></span></p> |
<h1><span style=""><a name="_GCT:_Gene_Cluster_Text file format "></a><a name="_GCT_File_Format"></a>GCT File Format</span></h1> | <h1><span style=""><a name="_GCT:_Gene_Cluster_Text file format "></a><a name="_GCT_File_Format"></a>GCT File Format</span></h1> | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The GCT format is a tab delimited file format that describes an expression dataset. It is organized as follows:</span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The GCT format is a tab delimited file format that describes an expression dataset. It is organized as follows:</span></p> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<p class="MsoListContinue"><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">#1.2 <o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> | <p class="MsoListContinue"><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">#1.2 <o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The <strong style="">second line</strong> contains numbers indicating the size of the data table that is contained in the remainder of the file. Note that the name and description columns are not included in the number of data columns. </span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The <strong style="">second line</strong> contains numbers indicating the size of the data table that is contained in the remainder of the file. Note that the name and description columns are not included in the number of data columns. </span></p> | ||
| − | <p | + | <p class="MsoNormal" style=""><span style="">Line format:<span style=""> </span>(</span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;"># of data rows) (tab) (# of data columns)<o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> |
| − | <p | + | <p class="MsoNormal" style=""><span style="">Example:<span style=""> </span></span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">7129 58 <o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> |
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The <strong style="">third line</strong> contains a list of identifiers for the samples associated with each of the columns in the remainder of the file. </span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The <strong style="">third line</strong> contains a list of identifiers for the samples associated with each of the columns in the remainder of the file. </span></p> | ||
| − | <p | + | <p class="MsoNormal" style=""><span style="">Line format:<span style=""> </span></span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">Name(tab)Description(tab)(sample 1 name)(tab)(sample 2 name) (tab) ... (sample N name) <o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> |
| − | <p | + | <p class="MsoNormal" style=""><span style="">Example:<span style=""> </span> </span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">Name Description DLBC1_1 DLBC2_1 ... DLBC58_0 <o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> |
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The <strong style="">remainder</strong> of the data file contains data for each of the genes. There is one line for each gene and one column for each of the samples. The first two fields in the line contain name and descriptions for the genes (names and descriptions can contain spaces since fields are separated by tabs). The number of lines should agree with the number of data rows specified on line 2. </span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The <strong style="">remainder</strong> of the data file contains data for each of the genes. There is one line for each gene and one column for each of the samples. The first two fields in the line contain name and descriptions for the genes (names and descriptions can contain spaces since fields are separated by tabs). The number of lines should agree with the number of data rows specified on line 2. </span></p> | ||
| − | <p | + | <p class="MsoNormal" style=""><span style="">Line format:<span style=""> </span></span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">(gene name) (tab) (gene description) (tab) (col 1 data) (tab) (col 2 data) (tab) ... (col N data) <o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> |
| − | <p | + | <p class="MsoNormal" style=""><span style="">Example:<span style=""> </span> </span><span style=""><code><span style="font-size: 10pt;">AFFX-BioB-5_at AFFX-BioB-5_at (endogenous control) -104 -152 -158 ... -44 <o:p></o:p></span></code></span></p> |
<h1><span style=""><a name="_RES_File_Format"></a>RES File Format</span></h1> | <h1><span style=""><a name="_RES_File_Format"></a>RES File Format</span></h1> | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The RES file format is a tab delimited file format that describes an expression dataset. It is organized as follows. The main difference between RES and GCT file formats is the RES file format contains labels for each gene's absent (A) versus present (P) calls as generated by Affymetrix's GeneChip software.</span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">The RES file format is a tab delimited file format that describes an expression dataset. It is organized as follows. The main difference between RES and GCT file formats is the RES file format contains labels for each gene's absent (A) versus present (P) calls as generated by Affymetrix's GeneChip software.</span></p> | ||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">[[image: rnk_format_snapshot.png]]</span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">[[image: rnk_format_snapshot.png]]</span></p> | ||
<h1><span style=""><a name="_MDB_File_Format"></a>MDB File Format</span></h1> | <h1><span style=""><a name="_MDB_File_Format"></a>MDB File Format</span></h1> | ||
| − | <p style="margin-bottom: 12pt; | + | <p class="MsoNormal" style="margin-bottom: 12pt;"><span style="">The MDB files contain an entire gene set database. Unlike the gmt/gmx files, the MDB files are designed to contain rich annotation about a gene set. They are xml formatted file based on the MSigDB Document Type Definition (DTD). Following is the MSigDB DTD and a sample MDB file based on that DTD.</span></p> |
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong>MSigDB DTD:<o:p></o:p></strong></span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style=""><strong>MSigDB DTD:<o:p></o:p></strong></span></p> | ||
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">[[image: msigdb_dtd_snapshot.png]]</span></p> | <p class="MsoNormal"><span style="">[[image: msigdb_dtd_snapshot.png]]</span></p> | ||
Revision as of 13:21, 28 March 2006
Contents
- 1 <a name="_Toc127331825">Data Formats Supported by GSEA</a>
- 2 <a name="_GCT:_Gene_Cluster_Text file format "></a><a name="_GCT_File_Format"></a>GCT File Format
- 3 <a name="_RES_File_Format"></a>RES File Format
- 4 <a name="_PCL_File_Format"></a>PCL File Format
- 5 <a name="_CLS_File_Format:_Categorical"></a>CLS File Format: Categorical
- 6 <a name="_CLS_File_Format:_Continuous"></a>CLS File Format: Continuous
- 7 <a name="_GMX_File_Format"></a>GMX File Format
- 8 GMT File Format
- 9 GRP File Format
- 10 <a name="_CHIP_File_Format"></a>CHIP File Format
- 11 <a name="_CSV_File_Format_(for Chip Files)"></a>CSV File Format (for Chip Files)
- 12 <a name="_RNK_File_Format"></a>RNK File Format
- 13 <a name="_MDB_File_Format"></a>MDB File Format
<a name="_Toc127331825">Data Formats Supported by GSEA</a>
For sample files, see http://wwwdev.broad.mit.edu/gsea/resources/datasets_index.html or, from within GSEA, select Help>Show GSEA Home Folder and go to the examples subfolder.
Expression data formats<o:p></o:p>
[[Data_formats#GCT_File_Format GCT: Gene Cluster Text file format (*.gct)]]
[[Data_formats#RES_File_Format RES: ExpRESsion (with P and A calls) file format (*.res)]]
[[Data_formats#PCL_File_Format PCL: Stanford cDNA file format (*.pcl)]]<a href="#_PCL_File_Format"></a>
Note: The GCT & RES expression formats supported by GSEA are identical to those supported by GenePattern.
Phenotype data formats<o:p></o:p>
[[Data_formats#CLS_File_Format:_Categorical CLS: Categorical (e.g tumor vs normal) class file format (*.cls)]]
[[Data_formats#CLS_File_Format:_Continuous CLS: Continuous (e.g time-series or gene profile) file format (*.cls)]]<a href="#_CLS_File_Format:_Continuous"></a>
Gene set database formats<o:p></o:p>
[[Data_formats#GMX_File_Format GMX: Gene MatriX file format (*.gmx)]]
[[Data_formats#GMT_File_Format GMT: Gene Matrix Transposed file format (*.gmt)]]
[[Data_formats#GRP_File_Format GRP: Gene set file format (*.grp)]]
[[Data_formats#MDB_File_Format MDB: Molecular signature database file format (*.mdb)]]<a href="#_MDB_File_Format"></a>
Note: Typically, you use the GMX or GMT formats to define gene sets.
Microarray annotation formats<o:p></o:p>
[[Data_formats#CHIP_File_Format CHIP: Chip file format (*.chip)]]
[[Data_formats#CSV_File_Format_.28for_Chip_Files.29 CSV: Comma Separated Version (*.csv)]]<a href="#_CSV_File_Format_(for Chip Files)"></a>
Ranked gene lists<o:p></o:p>
[[Data_formats#RNK_File_Format RNK: Ranked list file format (*.rnk)]]<a href="#_RNK_File_Format"></a>
<a name="_GCT:_Gene_Cluster_Text file format "></a><a name="_GCT_File_Format"></a>GCT File Format
The GCT format is a tab delimited file format that describes an expression dataset. It is organized as follows:
The first line contains the version string and is always the same for this file format. Therefore, the first line must be as follows:
#1.2 <o:p></o:p>
The second line contains numbers indicating the size of the data table that is contained in the remainder of the file. Note that the name and description columns are not included in the number of data columns.
Line format: (# of data rows) (tab) (# of data columns)<o:p></o:p>
Example: 7129 58 <o:p></o:p>
The third line contains a list of identifiers for the samples associated with each of the columns in the remainder of the file.
Line format: Name(tab)Description(tab)(sample 1 name)(tab)(sample 2 name) (tab) ... (sample N name) <o:p></o:p>
Example: Name Description DLBC1_1 DLBC2_1 ... DLBC58_0 <o:p></o:p>
The remainder of the data file contains data for each of the genes. There is one line for each gene and one column for each of the samples. The first two fields in the line contain name and descriptions for the genes (names and descriptions can contain spaces since fields are separated by tabs). The number of lines should agree with the number of data rows specified on line 2.
Line format: (gene name) (tab) (gene description) (tab) (col 1 data) (tab) (col 2 data) (tab) ... (col N data) <o:p></o:p>
Example: AFFX-BioB-5_at AFFX-BioB-5_at (endogenous control) -104 -152 -158 ... -44 <o:p></o:p>
<a name="_RES_File_Format"></a>RES File Format
The RES file format is a tab delimited file format that describes an expression dataset. It is organized as follows. The main difference between RES and GCT file formats is the RES file format contains labels for each gene's absent (A) versus present (P) calls as generated by Affymetrix's GeneChip software.
The first line contains a list of labels identifying the samples associated with each of the columns in the remainder of the file. Two tabs (\t\t) separate the sample identifier labels because each sample contains two data values (an expression value and a present/marginal/absent call).
Line format: Description (tab) Accession (tab) (sample 1 name) (tab) (tab) (sample 2 name) (tab) (tab) ... (sample N name)
For example: Description Accession DLBC1_1 DLBC2_1 ... DLBC58_0
The second line contains a list of sample descriptions. Currently, GSEA ignores these descriptions. Our RES file creation tool places the sample data file name and scale factors in this row, as shown below.
Line format: (tab) (sample 1 description) (tab) (tab) (sample 2 description) (tab) (tab) ... (sample N description)
Example: MG2000062219AA MG2000062256AA/scale factor=1.2172 ... MG2000062211AA/scale factor=1.1214
The third line contains a number indicating the number of rows in the data table that is contained in the remainder of the file. Note that the name and description columns are not included in the number of data columns.
Line format: (# of data rows)
For example: 7129
The remainder of the data file contains data for each of the genes. There is one row for each gene and two columns for each of the samples. The first two fields in the row contain the description and name for each of the genes (names and descriptions can contain spaces since fields are separated by tabs). The description field is optional but the tab following it is not. Each sample has two pieces of data associated with it: an expression value and an associated Absent/Marginal/Present (A/M/P) call. The A/M/P calls are generated by microarray scanning software (such as Affymetrix's GeneChip software) and are an indication of the confidence in the measured expression value. Currently, GSEA ignores the Absent/Marginal/Present call.
Line format: (gene description) (tab) (gene name) (tab) (sample 1 data) (tab) (sample 1 A/P call) (tab) (sample 2 data) (tab) (sample 2 A/P call) (tab) ... (sample N data) (tab) (sample N A/P call)
For example: AFFX-BioB-5_at (endogenous control) AFFX-BioB-5_at -104 A -152 A ... -44 A
<a name="_PCL_File_Format"></a>PCL File Format
The PCL file format is a tab delimited file format that describes an expression dataset. It is organized as follows. Support for this format is provided because several Stanford cDNA datasets are available in the PCL format.
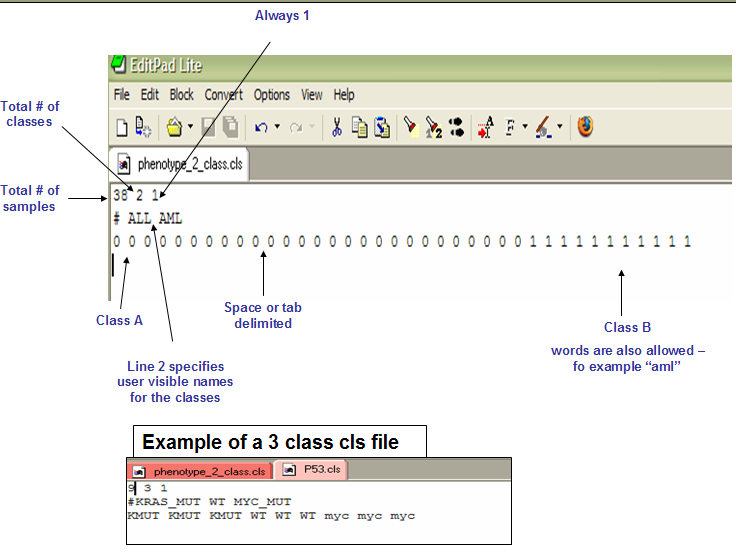
<a name="_CLS_File_Format:_Categorical"></a>CLS File Format: Categorical
The CLS file format defines phenotype (class or template) labels and associates each sample in the expression data with a label. The CLS file format uses spaces or tabs to separate the fields.
The CLS file format differs somewhat depending on whether you are defining categorical or continuous phenotypes. Categorical labels define discrete phenotypes; for example, normal vs tumor). For categorical labels, the CLS file format is organized as follows:
The first line of a CLS file contains numbers indicating the number of samples and number of classes. The number of samples should correspond to the number of samples in the associated RES or GCT data file.
Line format: (number of samples) (space) (number of classes) (space) 1
Example: 58 2 1
The second line in a CLS file contains names for the class numbers. The line should begin with a pound sign (#) followed by a space.
Line format: # (space) (class 0 name) (space) (class 1 name)
For example: # cured fatal/ref
The third line contains numeric class labels for each of the samples. The number of class labels should be the same as the number of samples specified in the first line.
Line format: (sample 1 class) (space) (sample 2 class) (space) ... (sample N class)
For example: 0 0 0 ... 1
<a name="_CLS_File_Format:_Continuous"></a>CLS File Format: Continuous
The CLS file format defines phenotype (class or template) labels and associates each sample in the expression data with a label. The CLS file format uses spaces or tabs to separate the fields.
The CLS file format differs somewhat depending on whether you are defining categorical or continuous phenotypes. Continuous phenotypes are used for time series experiments or to find gene sets correlations with a gene of interest (gene neighbors). For continuous labels, the CLS file format is organized as follows:
File:Cls numeric format snapshot.png
File:Cls time series format snapshot.png
<a name="_GMX_File_Format"></a>GMX File Format
The GMX file format is a tab delimited file format that describes gene sets. In the GMX format, each column represents a gene set; in the GMT format, each row represents a gene set. The GMX file format is organized as follows:
<a name="_GMT_File_Format"></a>Each gene set is described by a name, a description, and the genes in the gene set. GSEA uses the description field to determine what hyperlink to provide in the report for the gene set description: if the description is “na”, GSEA provides a link to the named gene set in MSigDB; if the description is a URL, GSEA provides a link to that URL.
GMT File Format
The GMT file format is a tab delimited file format that describes gene sets. In the GMT format, each row represents a gene set; in the GMX format, each column represents a gene set. The GMT file format is organized as follows:
<a name="_GRP_File_Format"></a>Each gene set is described by a name, a description, and the genes in the gene set. GSEA uses the description field to determine what hyperlink to provide in the report for the gene set description: if the description is “na”, GSEA provides a link to the named gene set in MSigDB; if the description is a URL, GSEA provides a link to that URL.
GRP File Format
The GRP files contain a single gene set in a simple newline-delimited text format. Typically, you use the GMT or GMX file formats to create gene sets, rather than using the GRP file format. The GRP file format is organized as follows:
<a name="_CHIP_File_Format"></a>CHIP File Format
The CHIP file contains annotation about a microarray. It should list the features (i.e probe sets) used in the microarray along with their mapping to gene symbols (when available). While this file is not used directly in the GSEA algorithm, it is used to annotate the output results and may also be used to collapse each probe set in the expression dataset to a single gene vector.
<a name="_CSV_File_Format_(for Chip Files)"></a>CSV File Format (for Chip Files)
The CSV file format is identical to the CHIP file, except that the values in each row are separated by commas rather than by tabs. This file format is primarily used for Affymetrix chips.
<a name="_RNK_File_Format"></a>RNK File Format
The RNK file contains a single, rank ordered gene list (not gene set) in a simple newline-delimited text format. It is used when you have a pre-ordered ranked list that you want to analyze with GSEA. For instance, you might have used your favorite tTest-like statistic to produce a ranked ordered gene list from your dataset which you now want to test for enrichment.
<a name="_MDB_File_Format"></a>MDB File Format
The MDB files contain an entire gene set database. Unlike the gmt/gmx files, the MDB files are designed to contain rich annotation about a gene set. They are xml formatted file based on the MSigDB Document Type Definition (DTD). Following is the MSigDB DTD and a sample MDB file based on that DTD.
MSigDB DTD:<o:p></o:p>
<o:p> </o:p>
Example of an MSigDB xml formatted file:<o:p></o:p>